Add Transformations#
The next step in defining a model is to transform the variables you’ve selected. This step is optional – for many models you may not need to make any modifications to the input variables.
To add a transformation, click Add Transformation and select an operation from the drop-down list.
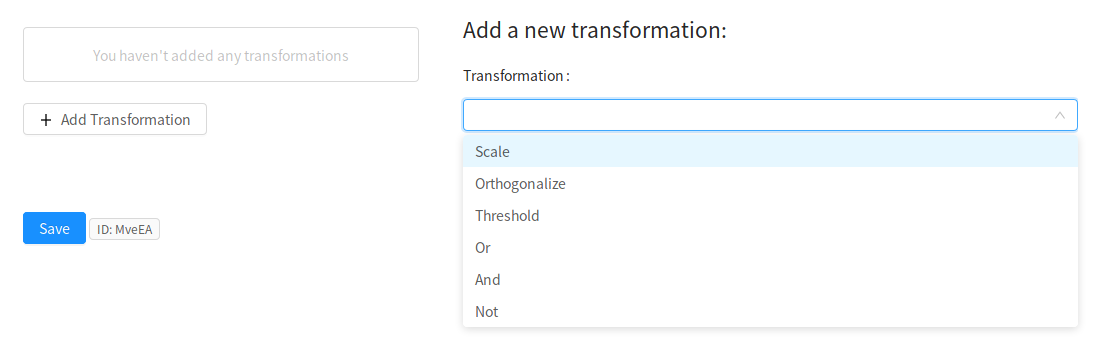
The transformations currently supported by Neuroscout are a subset of the complete set of transformations detailed in the BIDS StatsModel specification (in active development). As Neuroscout matures, the number of supported transformations will grow.
Transformation |
Description |
|---|---|
Scale |
Standardize the value of one or more variables. Can independently choose to demean and/or rescale. |
Orthogonalize |
Orthogonalizes one or more input columns with respect to one or more other columns. |
Select input#
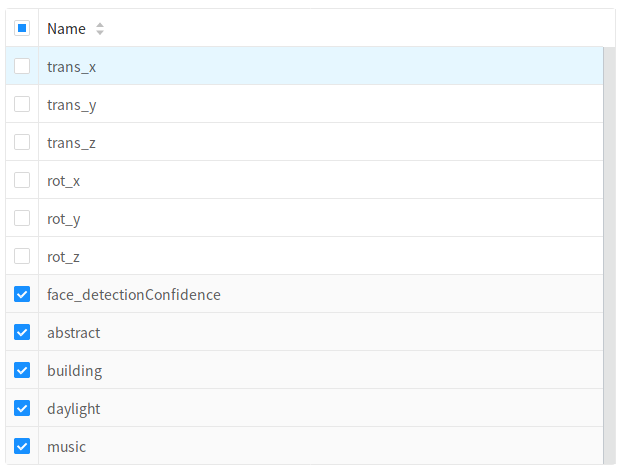
For all transformations, you must select which features this transformation will operate on.
Most operations will operate on each column independently, but specifying multiple columns will save you from having to specify the same operation for multiple predictors.
Transformation-specific options#
Most transformations additionally have specific options which you can specify.
Scale#
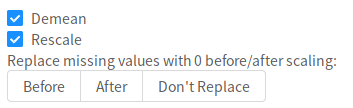
Demean- IfTrue, subtracts themeanfrom eachinputcolumn (i.e., appliesmean-centering).Rescale- IfTrue, divides eachcolumnby itsstandard deviation.ReplaceNA- Whether/when to replace missing values with0. If “Don’t replace”: no replacement is performed. If ‘before’: missing values are replaced with0’s beforescaling. If ‘after’: missing values are replaced with0afterscaling.
Note
If using only DummyContrasts, it is not necessary to scale variables, as the statistical maps we interpret are scale invariant. Scaling be necessary if computing contrasts between variables (which we don’t typically reccomend with naturalistic features).
However, it may be useful to use the scale transformation if there are missing values (NAs) in the variable. Replacing missing values with 0s after scaling effectively sets the values of NAs to the mean of that variable (for that run).
Orthogonalize#
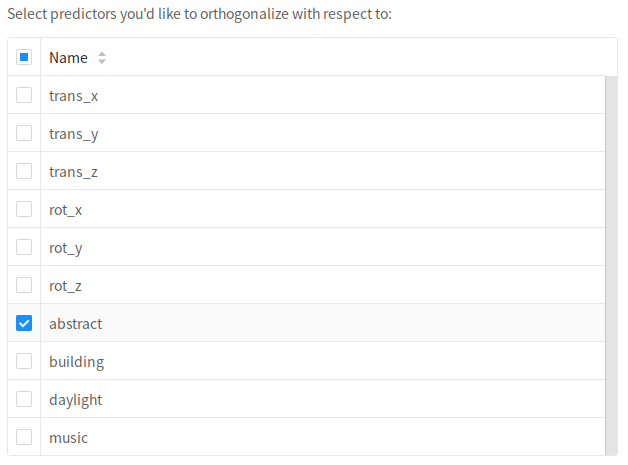
You must select the inputs to
orthogonalizewith respect to. Thetransformedvariable will beuncorrelatedto these variables.
Threshold#
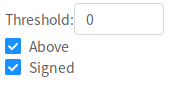
Threshold- The value tobinarizearound (values above will be assigned 1, values below will be assigned 0)Binarize- IfTrue,binarizesall non-zero values (i.e., every non-zero value will be set to1).Above- Specifies which values to retain with respect to the cut-off. IfTrue, all values above the threshold will be kept; ifFalse, all values below thethresholdwill be kept.Signed- Specifies whether to treat thethresholdassigned(default) orunsigned. For example, when passingabove=Trueandthreshold=3, ifsigned=True, all and only values above+3would be retained. Ifsigned=False, all absolute values> 3would be retained (i.e.,values in the range-3<X<3would be set to0).
Editing and ordering transformations#
It is important to note that transformations are applied sequentially, so the order of the transformation matters.
To re-order transformations you can drag and drop them in the list.
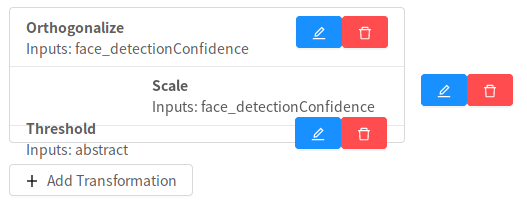
You can also remove transformations you’ve created using the trash icon, and edit existing transformations with the blue edit icon.